2011-AI
These are my notes from Sebastian Thrun and Peter Norvig's AI class. A course on Artificial Intelligence.
- AI class overview for an overview
- AI class journal for my journal
Course undertaken October to December 2011. Here goes nothing. :P
Week 1
Welcome to AI
Introduction
{{#ev:youtubehd|BnIJ7Ba5Sr4}}
Will deliver a good introduction to AI. Going to be a lot of work, but very rewarding.
New videos every week, and quizzes to test your knowledge built into the videos.
For the advanced version of the course are homework assignments and exams. These will be graded to determine if you can master AI the same way any good Stanford student could do it.
If you finish the course the lecturers will sign a letter of accomplishment and let you know what your rank in the class was.
Course Overview
{{#ev:youtubehd|Q7_GQq7cDyM}}
Purpose of the class:
- To teach the basics of AI artificial intelligence
- To excite you
Structure:
- Videos -> Quizzes -> Answer Videos
- Assignments (like quizzes but without the answers) and exams
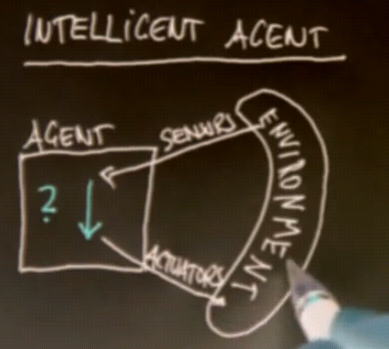
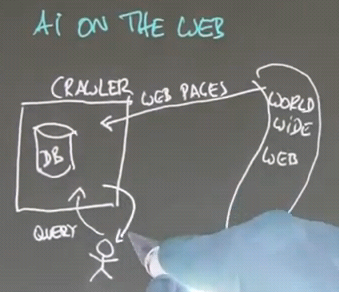
Intelligent Agents
{{#ev:youtubehd|cx3lV07w-XE}}
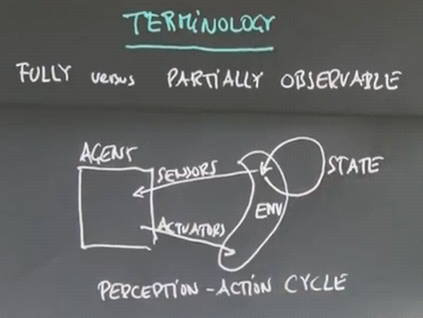
The agent has sensors that measure the environment, and actuators that can affect the environment.
The function that maps sensors to actuators is called the Control Policy of the agent.
This is the Perception-Action cycle:
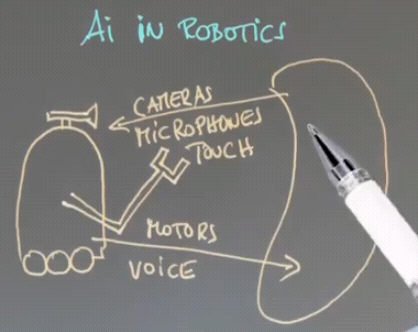
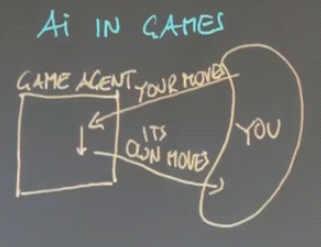
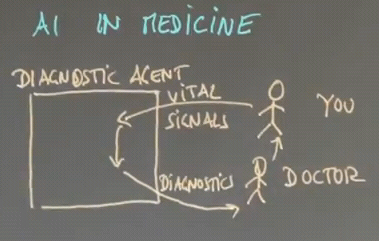
Applications of AI
{{#ev:youtubehd|N6JW8TQzbX8}}
Terminology
{{#ev:youtubehd|5lcLmhsmBnQ}}
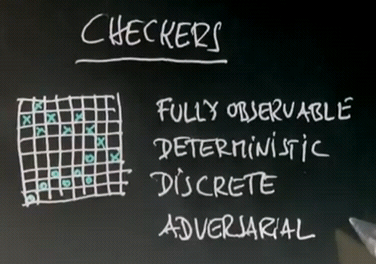
Checkers
{{#ev:youtubehd|qVppDRbx2kM}}
Poker Question
{{#ev:youtubehd|M_AdFAazf4k}}
{{#ev:youtubehd|DjILhASM3A8}}
Robot Car Question
{{#ev:youtubehd|vz-ERydsKLU}}
{{#ev:youtubehd|nOWCfVG0xNQ}}
AI and Uncertainty
{{#ev:youtubehd|ytw6_8a5Wls}}
Machine Translation
{{#ev:youtubehd|sPSN0aI0PgE}}
Chinese Translation
{{#ev:youtubehd|RWhwKudtixY}}
{{#ev:youtubehd|vvyaXxjsxBU}}
{{#ev:youtubehd|lFJey0tOvBg}}
Summary
{{#ev:youtubehd|mXM38kjzK-M}}
Problem Solving
Introduction
{{#ev:youtubehd|ZQmJuHtpGfs}}
In this unit we talk about problem solving. The theory and technology of building agents that can plan ahead to solve problems. In particular we're talking about problem solving where the complexity of the problem comes from the idea that there are many states, as in this problem here:
A navigation problem where there's many choices to start with and the complexity comes from picking the right choice now and picking the right choice at the next intersection and the intersection after that. Stringing together a sequence of actions.
This is in contrast to the type of complexity shown in this picture:
Where the complexity comes from the partial observability, that we can't see through the fog where the possible paths are or we can't see the results of our actions or even the actions themselves are not known. This type of complexity will be covered in another unit.
Here's an example of a problem:
This is a route finding problem.